Datasets
DDAD - Dense Depth for Autonomous Driving
DDAD is a new autonomous driving benchmark from TRI (Toyota Research Institute) for long range (up to 250m) and dense depth estimation in challenging and diverse urban conditions. It contains monocular videos and accurate ground-truth depth (across a full 360 degree field of view) generated from high-density LiDARs mounted on a fleet of self-driving cars operating in a cross-continental setting.
Overview
Dataset Name: DDAD - Dense Depth for Autonomous Driving
Organization: Toyota Research Institute (TRI)
Abstract: DDAD is a new autonomous driving benchmark for long range (up to 250m) and dense depth estimation in challenging and diverse urban conditions. It contains monocular videos and accurate ground-truth depth generated from high-density LiDARs mounted on a fleet of self-driving cars operating in a cross-continental setting.
Locations: United States (San Francisco, Bay Area, Cambridge, Detroit, Ann Arbor) and Japan (Tokyo, Odaiba)
Core Stats: 150 training scenes (12,650 frames), 50 validation scenes (3,950 frames), 3,080 test images, 360° coverage, 250m range, 10 Hz capture rate
License: Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
Dataset Specifications
# DDAD dataset configuration
ddad_config = {
"max_range": "250m",
"depth_precision": "sub-1cm",
"lidar_sensor": "Luminar-H2",
"camera_count": 6,
"camera_resolution": "2.4MP (1936 x 1216)",
"camera_type": "Global-shutter",
"camera_coverage": "360° (60° intervals)",
"capture_rate": "10 Hz",
"training_scenes": 150,
"training_frames": 12650,
"validation_scenes": 50,
"validation_frames": 3950,
"test_images": 3080,
"total_rgb_images": 75900
}
Sample & Results Showcase
Dataset Visualization
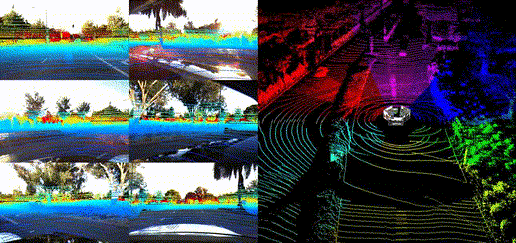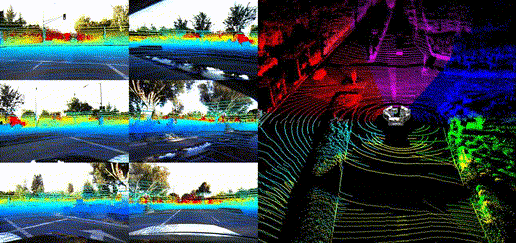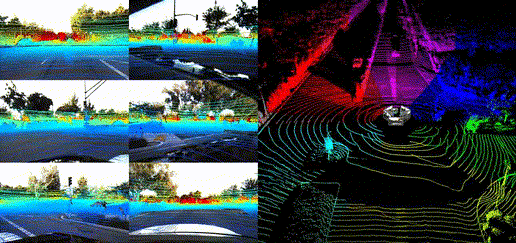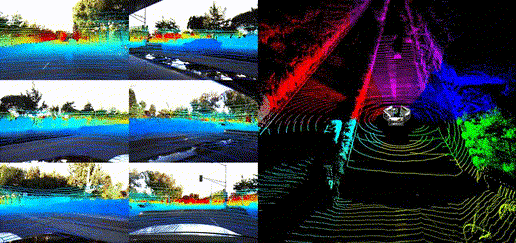
Panoramic Views
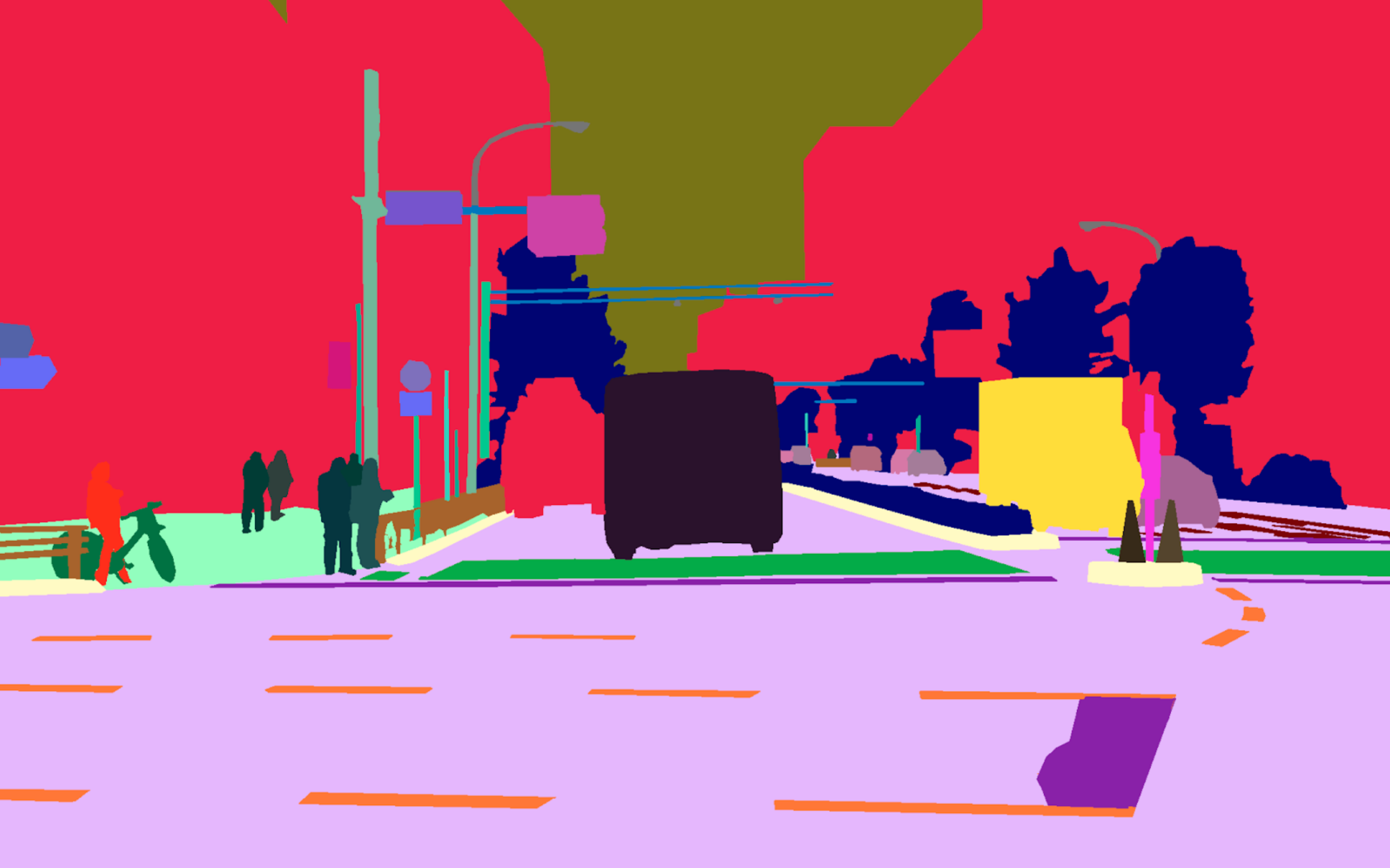
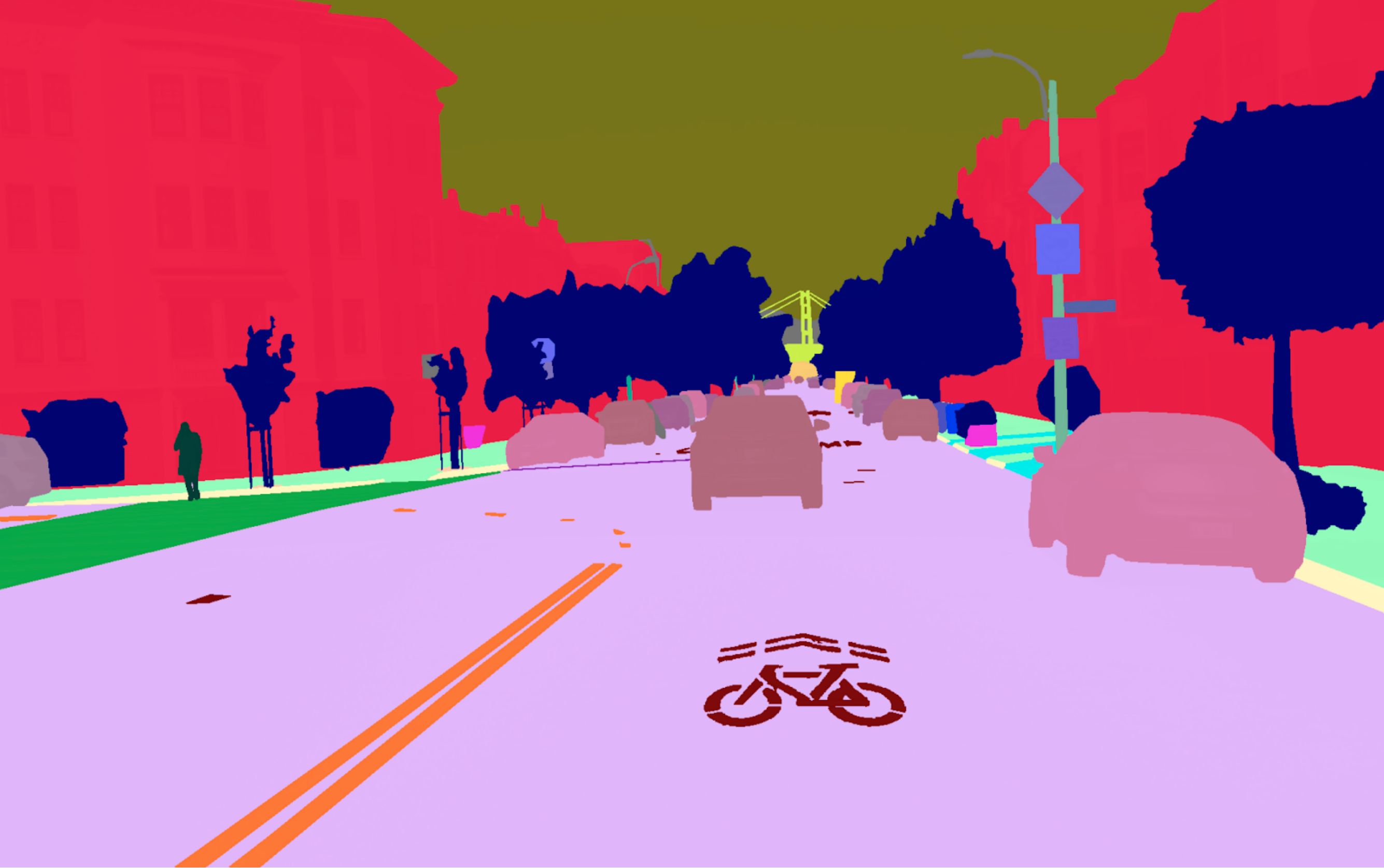
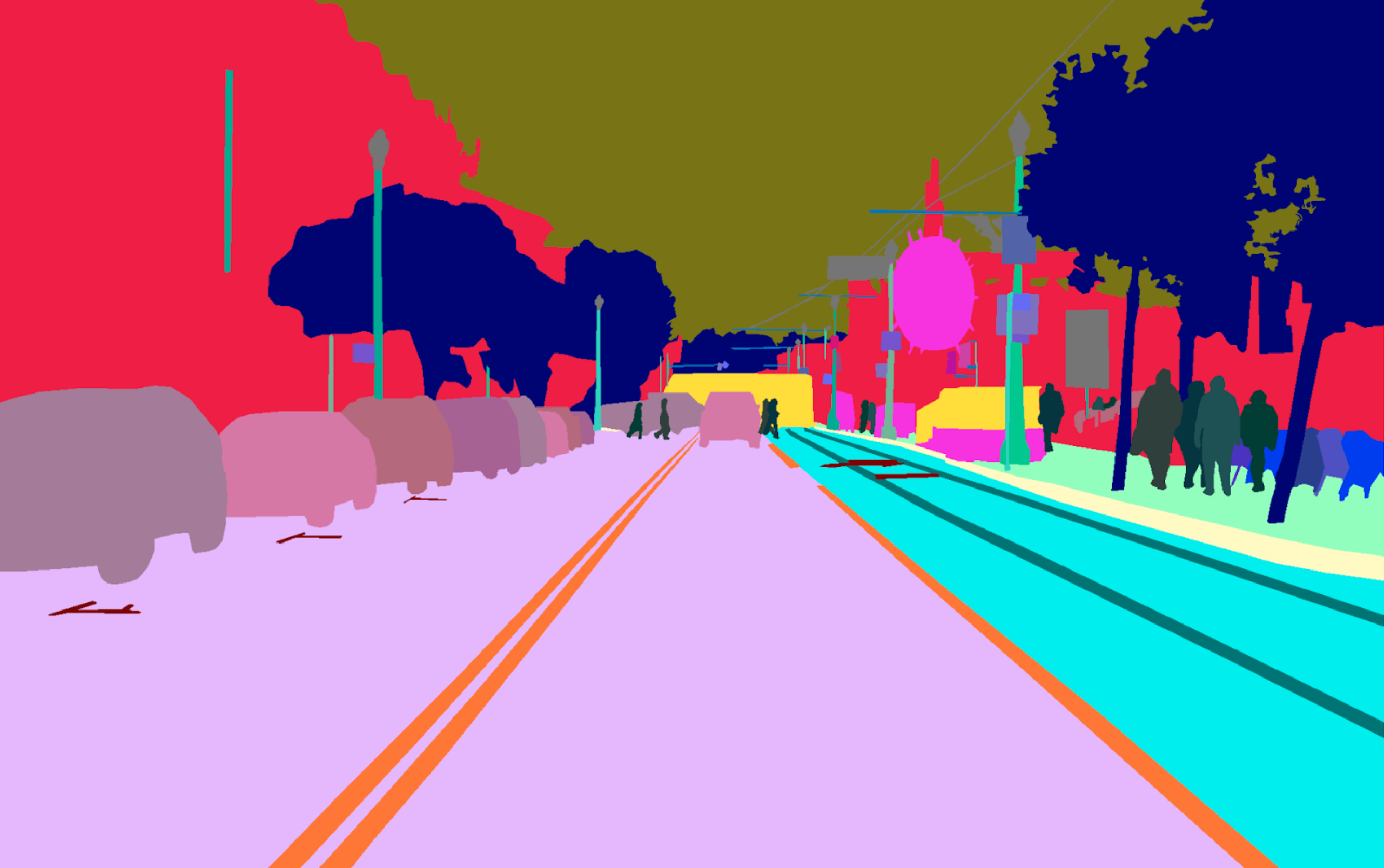


Location Showcases
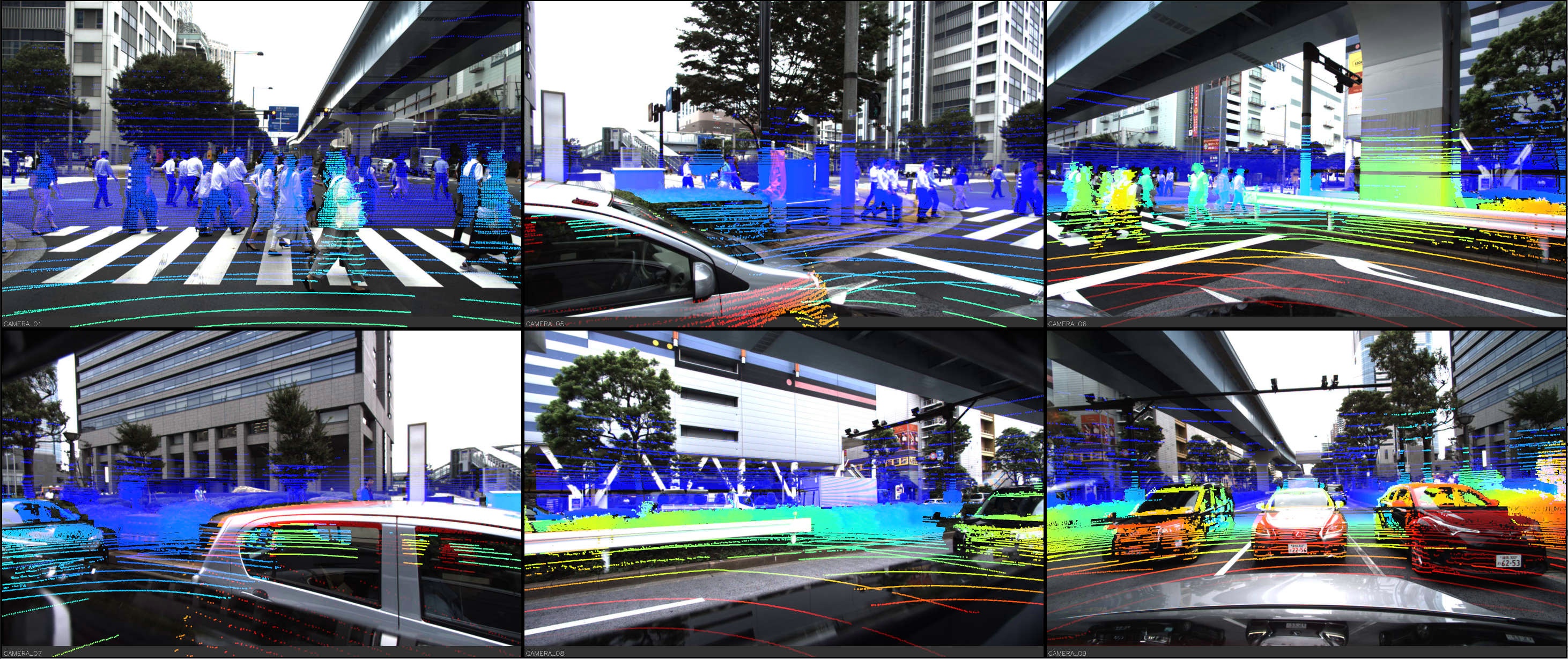
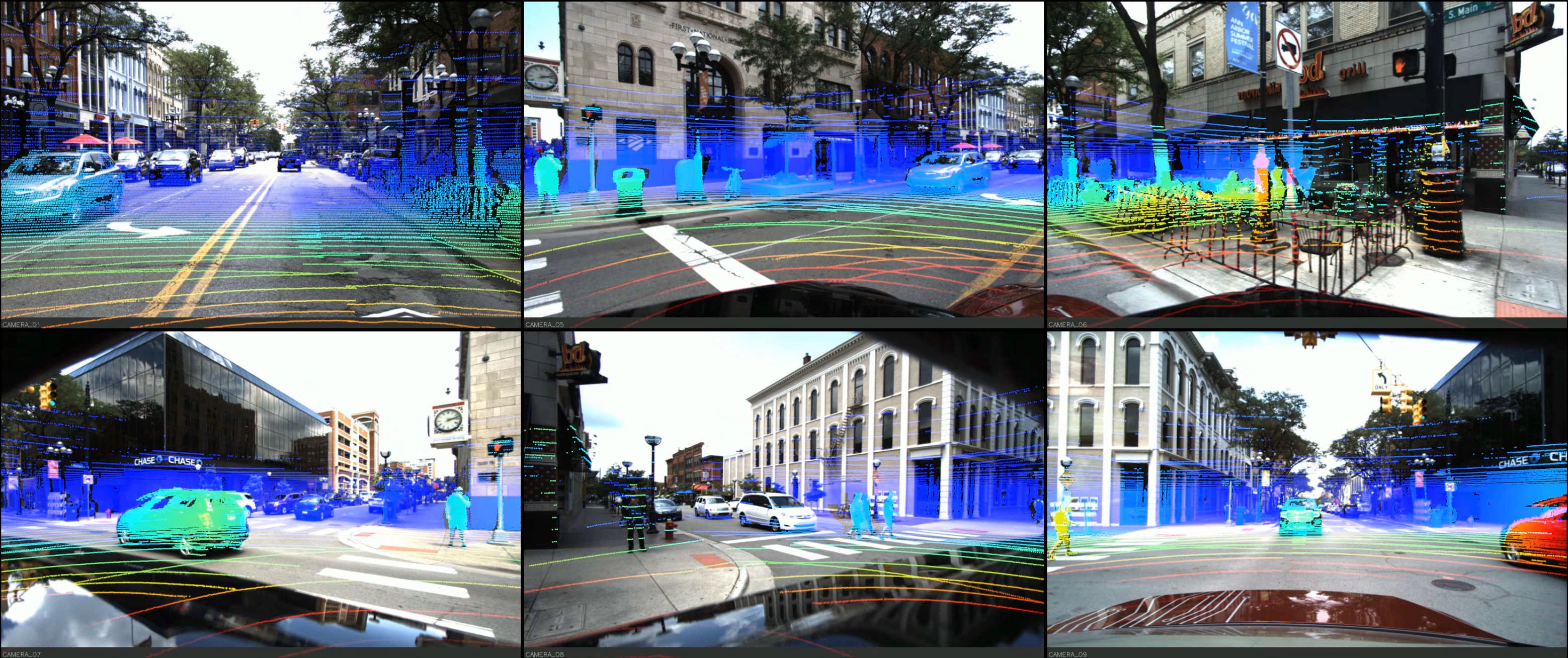

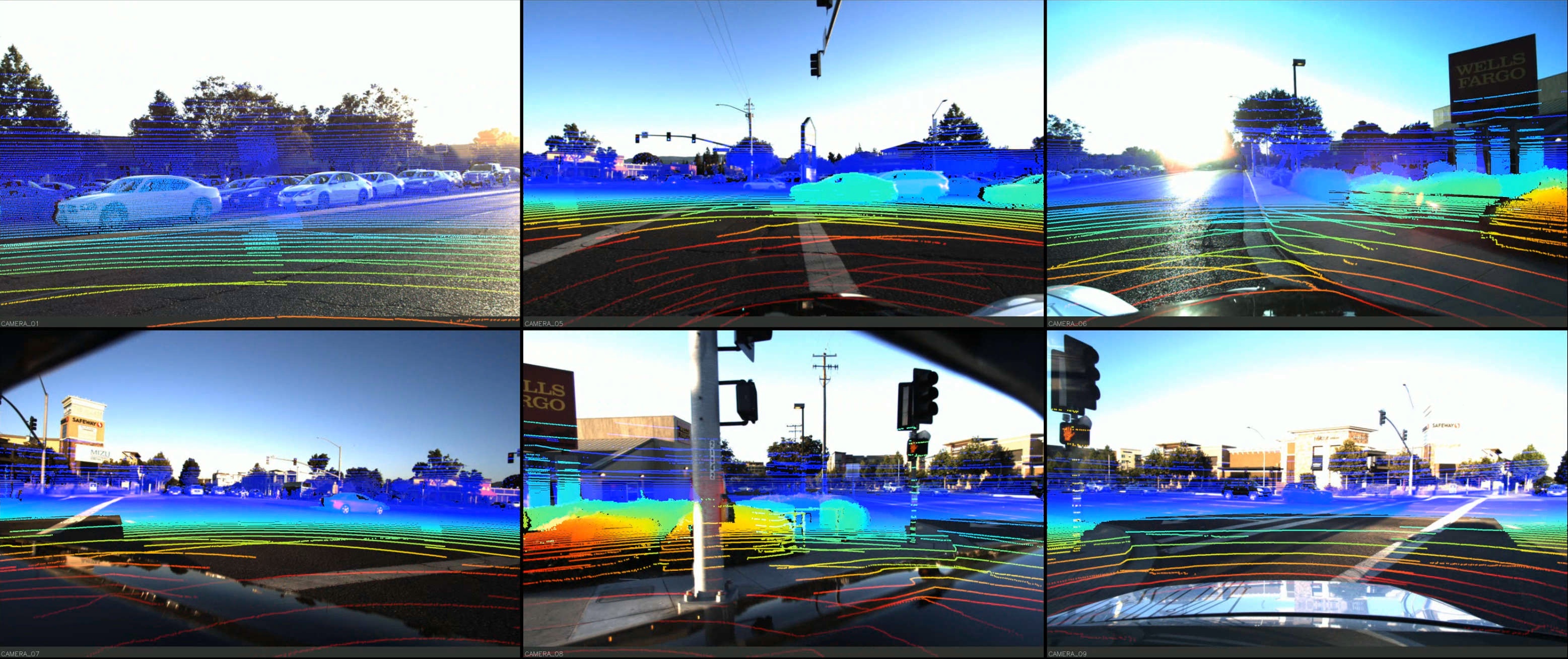

DDAD Depth Challenge
The DDAD depth challenge consists of two tracks:
- Self-supervised monocular depth estimation
- Semi-supervised monocular depth estimation
Methods are evaluated against ground truth LiDAR depth, with depth metrics computed per semantic class. The winner is chosen based on the abs_rel metric. Winners receive cash prizes and present their work at the CVPR 2021 Workshop "Frontiers of Monocular 3D Perception".
Experiment Description
Sensor Configuration
LiDAR: High-resolution, long-range Luminar-H2 sensors with:
- Maximum range: 250m
- Range precision: Sub-1cm
- Coverage: 360° (90° intervals)
- Frequency: 10 Hz scans
Cameras: Six calibrated cameras time-synchronized at 10 Hz:
- Resolution: 2.4MP (1936 x 1216)
- Type: Global-shutter
- Orientation: 60° intervals for 360° coverage
- Datum names:
camera_01,camera_05,camera_06,camera_07,camera_08,camera_09
Sensor Placement
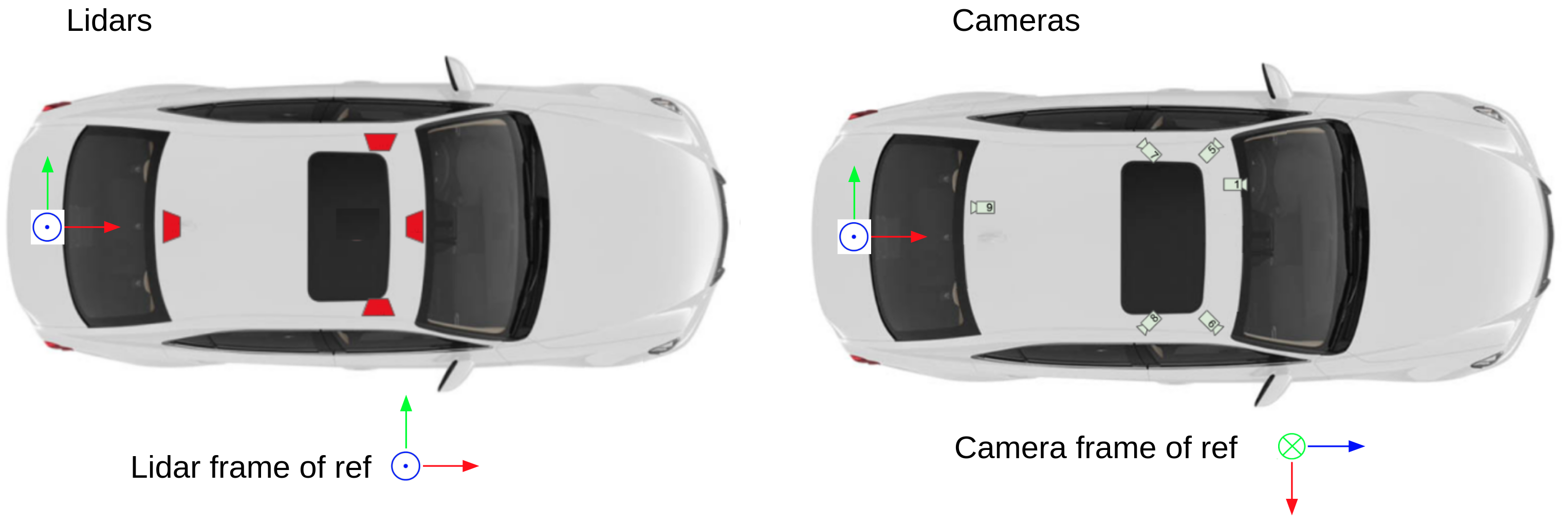
The figure shows the placement of DDAD LiDARs and cameras. Both LiDAR and camera sensors are positioned to provide 360° coverage around the vehicle. All sensor data is time-synchronized and reported at 10 Hz. The Luminar sensors report as a single point cloud in the vehicle frame of reference with origin on the ground below the center of the vehicle rear axle.
Dataset Structure
Training Set:
- 150 scenes (5 or 10 seconds long)
- 12,650 individual samples
- 75,900 RGB images (6 cameras per sample)
Validation Set:
- 50 scenes (5 or 10 seconds long)
- 3,950 individual samples
- 23,700 RGB images (6 cameras per sample)
Test Set:
- 3,080 images with intrinsic calibration
- 200 images with panoptic labels (similar to validation split)
- Ground truth depth and panoptic labels not publicly available
Dataset Statistics
Training Split
| Location | Num Scenes (50 frames) | Num Scenes (100 frames) | Total frames |
|---|---|---|---|
| SF | 0 | 19 | 1,900 |
| ANN | 23 | 53 | 6,450 |
| DET | 8 | 0 | 400 |
| Japan | 16 | 31 | 3,900 |
Total: 150 scenes and 12,650 frames
Validation Split
| Location | Num Scenes (50 frames) | Num Scenes (100 frames) | Total frames |
|---|---|---|---|
| SF | 1 | 10 | 1,050 |
| ANN | 11 | 14 | 1,950 |
| Japan | 9 | 5 | 950 |
Total: 50 scenes and 3,950 frames
Location Codes:
- USA: ANN - Ann Arbor, MI; SF - San Francisco Bay Area, CA; DET - Detroit, MI; CAM - Cambridge, Massachusetts
- Japan: Tokyo and Odaiba
Code Implementation
Dataset Loading
The data can be downloaded here: train+val (257 GB, md5 checksum: c0da97967f76da80f86d6f97d0d98904) and test.
To load the dataset, use the TRI Dataset Governance Policy (DGP) codebase:
from dgp.datasets import SynchronizedSceneDataset
# Load synchronized pairs of camera and lidar frames
dataset = SynchronizedSceneDataset(
'<path_to_dataset>/ddad.json',
datum_names=('lidar', 'CAMERA_01', 'CAMERA_05'),
generate_depth_from_datum='lidar',
split='train'
)
# Iterate through the dataset
for sample in dataset:
# Each sample contains a list of the requested datums
lidar, camera_01, camera_05 = sample[0:3]
# Access point cloud data
point_cloud = lidar['point_cloud'] # Nx3 numpy.ndarray
# Access camera images
image_01 = camera_01['rgb'] # PIL.Image
# Access depth maps (generated from lidar)
depth_01 = camera_01['depth'] # (H,W) numpy.ndarray
# Access camera intrinsics
intrinsics_01 = camera_01['intrinsics'] # 3x3 numpy.ndarray
# Access camera extrinsics
extrinsics_01 = camera_01['extrinsics'] # 4x4 numpy.ndarray
Evaluation Metrics
For detailed depth evaluation metrics, refer to the Packnet-SfM codebase.
We also provide an evaluation script compatible with our Eval.AI challenge:
cd evaluation
python3 main.py gt_val.zip pred_val_sup.zip semi
Evaluation Resources:
- Ground-truth depth maps for validation: gt_val.zip
- Example submission file: pred_val_sup.zip
Submission Format: Single zip file with same file name convention as test split (000000.png ... 003079.png). Each entry should be a 16-bit single channel PNG image. Predictions can be at full image resolution or downsampled (will be upsampled using nearest neighbor interpolation if needed).
IPython Notebook
The associated IPython notebook provides detailed instructions on:
- Instantiating the dataset with various options
- Loading frames with context
- Visualizing RGB and depth images for various cameras
- Displaying the LiDAR point cloud
Version History
| Date | Version | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | v1.0 | Initial release with training, validation, and test splits. CVPR 2021 challenge launch. |
Future Releases
- v1.1 (Planned): Additional urban locations and scenarios
- v2.0 (Planned): Extended range capabilities and additional sensor modalities
Contact & Support
Organization: Toyota Research Institute (TRI)
Website: https://www.tri.global/
Dataset Repository: TRI-ML/dgp
Challenge Platform: Eval.AI DDAD Challenge
Packnet-SfM Codebase: TRI-ML/packnet-sfm
Getting Help
For questions about dataset usage, evaluation metrics, or integration with your depth estimation pipeline, please refer to:
- The DGP codebase documentation
- The Packnet-SfM repository for training/inference/evaluation examples
- The Eval.AI challenge page for submission guidelines
References
3D Packing for Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation (CVPR 2020 oral)
Vitor Guizilini, Rares Ambrus, Sudeep Pillai, Allan Raventos and Adrien Gaidon
- Paper: arXiv:1905.02693
- Video: YouTube
@inproceedings{packnet,
author = {Vitor Guizilini and Rares Ambrus and Sudeep Pillai and Allan Raventos and Adrien Gaidon},
title = {3D Packing for Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation},
booktitle = {IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
primaryClass = {cs.CV},
year = {2020},
}
Privacy
To ensure privacy, the DDAD dataset has been anonymized using state-of-the-art object detectors for license plate and face blurring.
License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Dataset Impact
DDAD provides the first comprehensive benchmark for long-range (up to 250m) dense depth estimation in autonomous driving scenarios, enabling research into advanced monocular depth estimation methods for self-driving vehicles.
